SAP Landscape Management
SAP Landscape Management
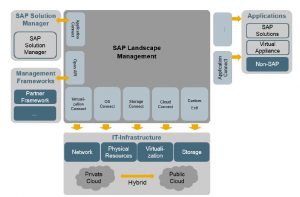
The SAP Landscape Management landscape is made up of the following building blocks:
- Managing system – The managing system is a virtual or physical server, installed with SAP Landscape Management or 7.4 for Java, where the SAP Landscape Management SCA files are deployed. It initiates the actions such as starting, stopping, and relocation of application instances.
- Managed SAP systems An SAP system consists of at least a database, a central instance, and a set of application servers running on one or more hosts (physical or virtual servers).We differentiate between the following installation variants:
- Adaptive enabled systems must be stored on central storage. To distribute the different parts of an SAP system on central storage, you use NAS (Network Attached Storage) or SAN (Storage Area Network). By using virtual hostnames for the SAP and database instances, you ensure that instances can be relocated from one operating system host to another.
- Virtualization based and traditionally installed systems are installed within a virtual machine (VM) and the corresponding virtualization manager is configured within SAP Landscape Management
- Infrastructure components
- Central storage management-The central storage management is used to create snapshots or copies of file systems. Leveraging storage technologies enables SAP Landscape Management to create copies of very large file systems very quickly and with a minimum of overhead. SAP Landscape Management relies on a central storage manager that can manage multiple central storage systems; SAP Landscape Management does not directly manage the individual storage systems.
- Virtualization management-Virtualization management is used by SAP Landscape Management to start, stop, and provision virtual hosts. This enables SAP Landscape Management to create new hosts when they are needed. It can be used to clone a complete host with the SAP system, in case it was installed within the virtual host.
- Central name server-The central name server is used to register host names for copied or cloned SAP systems.
- Central user management-Central user management is used to centrally register the operating system (OS) users needed for a copied SAP system.
Additional components
- System Rename-The software provisioning manager renames copied or refreshed systems. This includes changing the system ID, host name, and instance number from the source system to the target system. For this, a central share with the system rename functionality is mounted, and then the system rename is executed.
- ABAP post-copy automation-ABAP Post-copy automation (PCA) is executed after the system is renamed. It is responsible for cleaning up and reconfiguring the copied system.
- Java post-copy automation-Java PCA is executed after the system is renamed. It is responsible for cleaning up and reconfiguring copied systems.
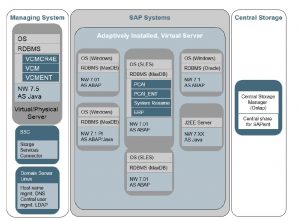
Here is an example for SAP S4 Landscape Environment:
Comments are closed.
