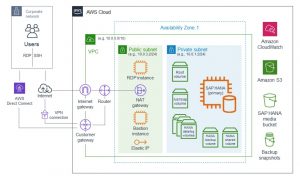
SAP AWS Architecture
It is ONLY a sample and it gives an idea on the AWS topology
SAP AWS Sample Architecture
SAP AWS Architecture
It is ONLY a sample and it gives an idea on the AWS topology

SAP AWS Sample Architecture
Prepackaged SAP Cloud Platforms – Interfaces can be built using SAP HCI
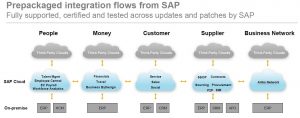
Prepackaged SAP Cloud Platforms
SAP SuccessFactors Processes
SAP SuccessFactors processes and interfaces with legacy/3rd party Payroll and HR systems like ADP Kronos etc
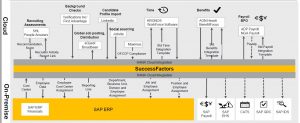
SAP Success Factor Processes
SAP HANA Cloud Integrator (HCI) Architecture- SAP Concur, SAP Success Factor, NonSAP interfaces
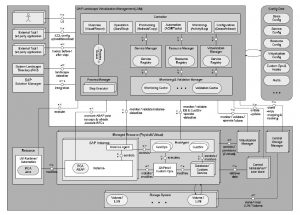
SAP Landscape Management
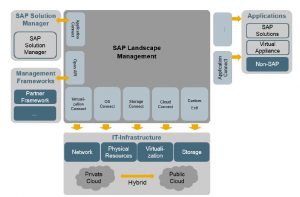
The SAP Landscape Management landscape is made up of the following building blocks:
Additional components
Here is an example for SAP S4 Landscape Environment:
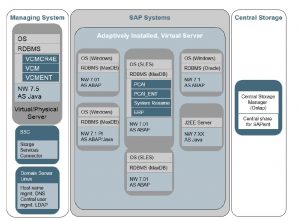
SAP S4 HANA Migration(N, N+1 Strategy)
This can be followed for Data Center migration also
Here is a detailed steps as recommended by SAP
SAP Cloud Platform Integration Features
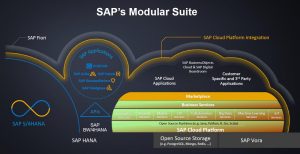
SAP Cloud Platform Interfaces technology
SAP_Cloud_Platform_Integration_ Features
Get in touch with kumaran27@hotmail.com if you need additional details on this platform features details
AWS Reference Architecture
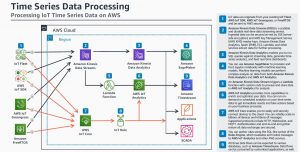
AWS Reference Architecture
SAP S4 HANA Product suite and Business Functionality
SAP S4 HANA 1610/1709 Conversion Projects – The below data gives an idea for Source and Target SAP S4 HANA environments ; This helps for SAP S4 Target Environment Sizing when we do Conversion projects
| Source System | Target SAP S4 System Configuration |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 6 Oracle DB 60 TB database |
S/4HANA 1610 1,300 active users 36 TB memory 13,6 TB database SAP HEC |
| SAP ERP DB2 database 38 TB database |
S/4HANA 1610 3 x 8 TB memory 8.5 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 Oracle database 16.4 TB database 300m VBAP entries |
S/4HANA 1709 20,000 active users 12 TB memory 6.3 TB database 800m ACDOCA entries 200m MATDOC entries |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 HANA DB |
S/4HANA 1610 4,100 active users 6 TB memory 4.5 TB database |
| S/4HANA Finance 1503 2.8b BSEG entries 750m COEP entries 630m MSEG entries |
S/4HANA 1709 2,500 active users 16 TB memory 4.4 TB database 3.4b ACDOCA entries 700m MATDOC entries |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 HANA DB 2.6 TB database |
S/4HANA 1610 12,300 active users 10.2 TB memory 3.7 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 HANA database 4 TB database |
S/4HANA 1709 15,200 active users 4 TB memory 3 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 Oracle DB 7 TB database |
S/4HANA 1610 19,200 active users 4 TB memory 2.3 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 HANA DB |
S/4HANA 1610 2,600 active users 3 TB memory 2.1 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 HANA DB |
S/4HANA 1610 8,000 active users 6 TB memory 2 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 HANA DB |
S/4HANA 1610 3,300 active users 6 TB memory 1.3 TB database |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 8 HANA DB 28,000 custom objects 210m BSEG entries 157m COEP entries 42m MSEG entries |
S/4HANA 1709 3,000 active users 3 TB memory 1.2 TB database 850m ACDOCA entries 43m MATDOC entries |
| S/4HANA Finance HANA database 1 TB database 2,600+ custom objects 572m BSEG entries 120m MSEG entries |
S/4HANA 1709 3,300 active users 4 TB memory 1 TB database 1.5b ACDOCA entries 120m MATDOC entries |
| ERP 6 EhP 7 SQL Server database 9,200 custom objects 310m BSEG entries 140m MSEG entries |
S/4HANA 1709 1,100 active users 3 TB memory 1 TB database 1b ACDOCA entries 139m MATDOC entries |
| ERP 6.0 EhP 7 Oracle DB 12 TB database |
S/4HANA 1610 107,000 active users 12 TB memory 1 TB database |
SAP Landscape Management
SAP Landscape Management consists of the following components:
Multi-AZ, single-node, high availability architecture for SAP HANA on AWS
The Multi-Available Zone, single-node, high availability SAP S4 HANA Environment Setup is as given below
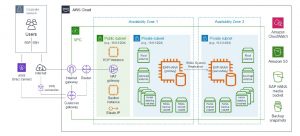
Single-AZ, multi-node architecture for SAP HANA on AWS
The Single-AZ, multi-node deployment option provisions up to five EC2 instances with any choice of Amazon EBS storage and operating system to host the SAP HANA platform on a cluster of servers. All the SAP HANA servers in the cluster are deployed into the same subnet.
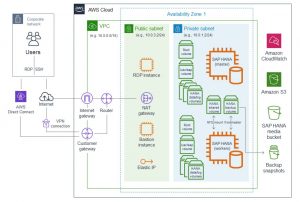
Single-AZ, single-node architecture for SAP HANA on AWS
The Single-AZ, single-node deployment option provisions a single EC2 instance with Amazon EBS storage and operating system to host the SAP HANA platform. The Quick Start follows security best practices by establishing a VPC with public and private subnets. For secure access, the SAP HANA server is placed in the private subnet, which is not directly accessible from the internet. We can install SAP HANA Studio manually in the optional Windows Server instance that is provisioned in the public subnet. For SSH access to the SAP HANA server, you can use the bastion host or an SSH client on the optional Windows Server instance.